Bulgaria is a country in the eastern Balkans, bordering Turkey, Romania, Greece, and Serbia. It occupies an important position on the Balkan Peninsula and has access to the Black Sea. Among other Balkan states, Bulgaria has a relatively higher Corruption Perception Index of 45, compared to Albania’s index of 37 or the regional average of 43. The country is considered upper-middle-income according to the World Bank, with a relatively low budget deficit of -2.81% in 2021.
Bulgaria has a high level of urbanization, according to World Bank data, it has 136 cities. Seven of them have a population of more than 100,000. In the National Development Program Bulgaria 2030, the perspective is expected to include smart city technology as well. But what is the situation with usage of urban smart technology right now?
We analyzed the programs and projects in the Bulgarian cities (information taken from open sources) and received a heterogeneous picture. Results showed that at least two cities have a high level of developmental technological features for urban sustainability. Additionally, we found some other cases with fragmented usage of smart technologies. However, most of Bulgarian cities are not on the path to a sustainable future.
We begin our review with Burgas. According to experts, Burgas is the smartest city in Bulgaria, renowned for promoting sustainable development through its projects and strategies. Burgas is located on the southeastern shore of Bulgaria, by the Black Sea. It is the fourth-largest city in Bulgaria, with a population of around 196,000 (as of 2024). Its location along the coastline gives the city the status of Bulgaria’s gateway to the sea. Burgas is an industrial hub and, in addition, attracts many tourists each year with its cultural and natural landmarks.

Transport
Burgas is known for its smart city solutions, particularly in improving mobility and infrastructure platforms, like those of other Western European cities. Renovation and reconstruction of the public transport system is an important achievement for the city. Burgas became the first city in Bulgaria to include a bike-sharing service in its mobility policy. The initial project was funded by the Global Environmental Fund and aimed at expanding the city’s infrastructure. Today, Burgas not only offers an extensive traditional bike-sharing system but also features an e-bike system, providing both tourists and residents with healthy and eco-friendly ways to get around the city. “Velo Burgas,” with eight access points for renting bikes throughout the city, continues to expand, enhancing the city’s reputation as a greener and more sustainable hub for mobility.
Digitalization
The heart of urban innovation in Burgas is the digital hub Smart Burgas. It provides a convenient solution for both tourists and residents. With just one click, you can access everything about the city—from CO2 emission levels in the atmosphere to concert schedules. This interactive platform brings together information related to the urban environment. It offers comprehensive details about city life, including transportation traffic, weather updates, news, various types of maps, document management, and bike rentals.
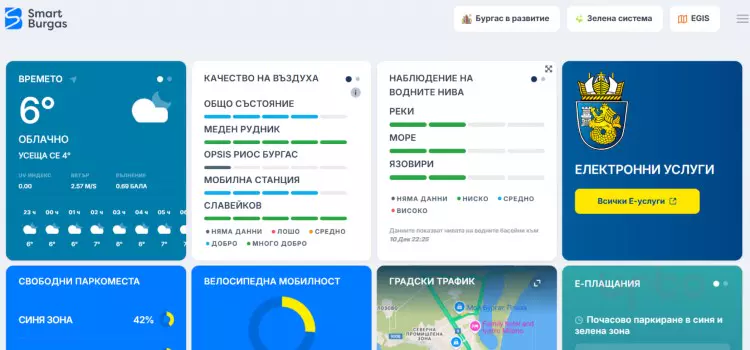
The urban hub collects data from a variety of smart devices installed throughout the city. These high-tech sensors send information about air and water quality, parking and traffic conditions, bike rentals, and even video surveillance of city streets. The SMART Burgas platform integrates smart systems to improve city management and transparency. Additionally, it provides a shared space where citizens and experts can access integrated city data, watch live streams, learn about municipal services, and participate in urban planning surveys.
Partnership
The strength of Burgas’ urban policy lies in its involvement in various partnership networks, which facilitates the integration of fresh innovations into the urban decision-making process.
Burgas became a part of the network “Sharing Cities” which includes Lisbon, Warsaw, Bordeaux, Milan, and London. This network is believed to have been established for international collaboration to achieve “smart and sustainable cities”. Burgas is evolving into a user-centric city service. They are creating a sharing platform based on open data. With the additional support from the EU, the local municipality has implemented many different smart infrastructure solutions, such as sustainable energy systems, smart lamp posts, and others. One of the drivers of the development of smart Burgas is the inclusion of the city in numerous networks of interaction and acceleration. Burgas has also signed the Green City Accord among other European cities, which helps to achieve the cleanliness and healthiness of the city. Intensive collaboration with other European cities helps Burgas stay ahead in its sustainable development using smart technologies.
Civil engagement
Burgas’ civil society demonstrates strong engagement in addressing waste management challenges. For example, “Бургас Рециклира” is a well-known citizen initiative focused on waste separation. This initiative began as a voluntary community of active citizens who promoted the idea of waste reduction and responsible waste management. In November, the Burgas Municipality received an award from the French Institute in the “Waste and Recycling” category, with citizen initiatives making a significant contribution to this achievement.

Smart technologies increasingly demand the participation of many different stakeholders. One of the goals of sustainable development concerns citizen engagement in the decision-making process. However, for this, changing political and citizens’ cultural attitudes is needed. This work continues, and it focuses on improvements in citizen information and participation in enhancing city life.
Air and water quality
Like other Balkan countries, Bulgaria and its city of Burgas demonstrate relatively bad air quality. Moreover, with the arrival of winter, the heating season begins, and many households rely on domestic heating with solid fuels, which contributes to air pollution in the cities. To address this, more than 4,000 households in the municipality are part of the “Environment” program, co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund of the European Union under the initiative “For Cleaner Air!” The project aims to change the population’s behavior and introduce an effective mechanism for investing in alternative heating systems. Air pollution issues are also addressed in other projects, such as the CLEAR-CITIES project, which aims to improve waste management policies and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.

Burgas is a major port and transportation center, which has led to the influence of some companies on the environment. For many years, social media users have expressed concern about the unpleasant smells from the oil refining companies near the city. This issue is still unresolved. Commentators on social media have suggested that the company could renovate the facilities used for oil storage.
A comprehensive strategy for the development of Burgas is available to everyone on the website: https://plan.smartburgas.eu/. The main idea of this plan is the creation of a framework for future achievements of the smart and sustainable city of Burgas. Almost all indicators of a sustainable city are in Burgas, it is on the path to a sustainable future. Burgas gives us the chance to see developed infrastructure and urban smart technologies. The development of Burgas’ urban space continues to progress in a smart direction. For example, in Burgas, old wood and coal heating appliances have been replaced with new, environmentally friendly ones, which have improved air quality. Energy efficiency measures in buildings have become a priority for 4200 households. While sustainable initiatives have been successfully implemented, some challenges in the city’s development strategy are inevitable. Nonetheless, Burgas is steadily advancing towards becoming a smart and sustainable city. This city is one of the few examples of a comprehensive approach to urban space development, considering the goals of sustainable development.


